A Detailed Guide to ETF Investment with Navia
In the ever-evolving investment landscape, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) have gained substantial popularity among both novice and seasoned investors. These versatile financial instruments offer a cost-effective and diversified way to participate in the financial markets. If you’re eager to explore ETF investment, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about ETFs, from their basics to advanced strategies.
What Is an ETF Investment?
At its core, an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a financial product that combines the benefits of a mutual fund and a stock. Essentially, it’s a collection of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities, bundled together and traded on stock exchanges, just like individual stocks. ETFs are designed to replicate the performance of a particular index, sector, commodity, or asset class.
Understanding ETFs
To truly grasp the concept of ETFs, let’s break down some of their fundamental characteristics:
1. Liquidity: ETFs are traded on stock exchanges throughout the trading day, making them highly liquid. This means you can buy or sell them at prevailing market prices, just like stocks.
2. Diversification: ETFs offer instant diversification because they hold a basket of assets. This spreads risk and can help protect your investments from the volatility of individual securities.
3. Transparency: ETFs disclose their holdings daily, allowing investors to know exactly what assets are held within the fund. This transparency aids in making informed investment decisions.
4. Cost-efficiency: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. This cost advantage can lead to better long-term returns for investors.
5. Tax Efficiency: Due to their unique structure, ETFs can be more tax-efficient than mutual funds, as they often generate fewer capital gains distributions.
Types of ETFs
ETFs come in various flavors, catering to diverse investment objectives. Here are some common types:
1. Equity ETFs
Equity ETFs invest primarily in stocks. They can track specific stock market indices, such as the S&P 500, or focus on certain sectors, industries, or regions.
2. Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs invest in a variety of bonds, including government, corporate, municipal, or international bonds. They provide exposure to the fixed-income market.
3. Commodity ETFs
Commodity ETFs offer exposure to physical commodities like gold, oil, or agricultural products. They can be an effective way to diversify a portfolio.
4. Sector ETFs
Sector ETFs concentrate on specific industry sectors, allowing investors to bet on the performance of a particular area of the economy.
5. International ETFs
International ETFs invest in foreign markets and can provide diversification benefits, as well as opportunities for growth in global economies.
6. Smart Beta ETFs
Smart Beta ETFs aim to outperform traditional market-cap-weighted indices by using alternative weighting methodologies based on factors like value, quality, or momentum.
How to Buy ETFs
Investing in ETFs is a straightforward process. Here’s how you can get started:
Online vs. Traditional Brokerage
You can buy ETFs through demat account or traditional brokerage firms. Online brokerages often offer lower trading fees and user-friendly platforms, making them a popular choice for DIY investors. Traditional brokerages may provide more personalized services but typically come with higher costs.

Factors to consider for ETF investment
Before investing in an ETF, consider the following factors:
1. Expense Ratio: Look for ETFs with low expense ratios, as high fees can eat into your returns over time.
2. Liquidity: Check the average trading volume of the ETF investment to ensure you can buy or sell shares without any issues.
3. Tracking Error: Evaluate how closely the ETF’s performance matches its underlying index.
4. Holdings: Examine the ETF’s holdings to ensure they align with your investment goals.
5. Dividend Yield: If you’re seeking income, look for ETFs with a competitive dividend yield.
Pros and Cons of Investing in ETFs
Like any investment vehicle, ETF investment comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
🔹Diversification: ETFs offer instant diversification across a range of assets.
🔹Liquidity: They can be easily bought or sold during market hours.
🔹Low Costs: ETFs typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
🔹Transparency: Investors can see the ETF’s holdings daily.
🔹Tax Efficiency: ETFs are often more tax-efficient than mutual funds.
Cons:
🔹Brokerage Commissions: While many online brokers offer commission-free ETF trading, some may still charge fees.
🔹Tracking Error: ETFs may not perfectly replicate their underlying index’s performance.
🔹Limited Control: Investors have no say in the management decisions of the underlying assets.
🔹Intraday Trading Risks: Excessive trading of ETFs can lead to high trading costs and potential tax consequences.
Actively Managed ETFs
While most ETFs passively track an index, some are actively managed by professional portfolio managers. These managers aim to outperform the market through active stock selection and trading strategies. Actively managed ETFs tend to have higher expense ratios than their passive counterparts.
Special Considerations
Creation and Redemption
The unique structure of ETFs involves a creation and redemption process that helps keep their market prices close to the net asset value (NAV). Authorized Participants (usually large financial institutions) create or redeem ETF shares based on demand. This process keeps the ETF’s market price in line with its underlying assets.
Mutual Funds and Stocks
ETFs share similarities with both mutual funds and individual stocks, combining the diversification of mutual funds with the flexibility of trading stocks. Understanding these aspects can help you make informed investment decisions.
In conclusion, Exchange Traded Funds are versatile investment tools that offer diversification, liquidity, and cost-efficiency. Whether you’re a beginner looking to start investing or an experienced investor seeking to enhance your portfolio, ETFs can play a valuable role in achieving your financial goals. As with any investment, it’s crucial to do your research, understand your risk tolerance, and consider your long-term objectives when incorporating ETFs into your investment strategy.
ETFs are bought and sold on exchanges at the market price. The market price can change throughout the trading day. Factors like supply, demand, and changes in the value of an ETF investment can affect the market price. The bid is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay if you want to sell your ETF units.
The Rise of Active ETFs
Traditionally, ETFs have been associated with passive investing, where they aim to replicate the performance of a specific index. However, active ETFs are changing the game. Unlike their passive counterparts, active ones are managed by portfolio managers who make strategic investment decisions with the goal of outperforming the market.
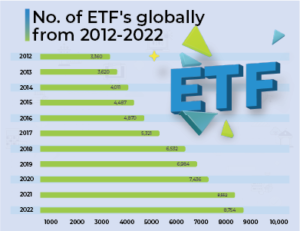
Projected Growth
A key indicator of this shift is the projected growth of ETFs in the coming years. By 2027, it is estimated that ETFs will account for a substantial 24% of total fund assets, a notable increase from their current 17% share. This anticipated growth underscores the increasing popularity and acceptance of ETFs as a favored investment vehicle.
Maximize your returns with Exchange Traded Funds using our zero-brokerage trading app
How to Invest in ETFs Using Navia, the Trading App Powered by Navia
Introduction
Investing in Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) through us is a straightforward process that provides access to a diversified portfolio of assets.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Account Setup:
🔹Start by opening an account with Navia if you don’t already have one.
🔹Complete the necessary eKYC (Know Your Customer) requirements to activate your trading account.
Download the Navia App:
🔹Visit your device’s app store (iOS or Android) and download the “Navia” trading app by Navia.
Log In:
🔹Launch the Navia app and log in using your Navia Markets credentials.
Funding Your Account:
🔹Ensure that you have sufficient funds in your trading account to invest in ETFs.
🔹You can transfer funds to your Navia account securely through various payment methods.
Research and Selection:
🔹Utilize the research tools and resources provided by the app to identify ETFs that align with your investment goals.
🔹Consider factors like expense ratios, liquidity, and asset allocation.
Placing Orders:
🔹Select the ETF you wish to invest in and choose the number of units or shares you want to purchase.
🔹Place a market order (buy at the current market price) or limit order (specify a desired purchase price).
Review and Confirm:
🔹Double-check your order details to ensure accuracy, including the ETF name, quantity, and order type.
🔹Confirm your order to execute the trade.
Monitor Your Portfolio:
🔹Keep track of your ETF investment through the Navia app.
🔹Monitor performance, review holdings, and consider rebalancing your portfolio as needed.
Diversification:
🔹Explore various ETFs to build a diversified investment portfolio that suits your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Exit Strategy:
🔹When it’s time to sell your ETF holdings, use the Navia app to place sell orders following a similar process.
Tax Considerations:
🔹Be aware of tax implications related to ETF investments and consult a tax professional if necessary.
Customer Support:
🔹If you encounter any issues or have questions about ETF investing on Navia, reach out to our customer support for assistance.
Conclusion:
Navia offers a user-friendly platform through the Navia app for investing in ETFs. By following these steps, you can start building a diversified ETF portfolio tailored to your financial objective.
We’d Love to Hear from you-
DISCLAIMER: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. The securities quoted are exemplary and are not recommendatory. Brokerage will not exceed the SEBI prescribed limit.





