Small-Cap vs Large-Cap Equity Mutual Funds Which is Right for You?
Introduction
When it comes to investing in equity mutual funds, one of the primary decisions investors faces is whether to choose small-cap vs large-cap funds. Each option offers distinct advantages and risks, making it essential for investors to understand their individual financial goals and risk tolerance. In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of small-cap and large-cap equity mutual funds and provide insights to help investors make informed decisions.
How to Calculate Market Cap
Market capitalization measures a company’s value by evaluating the market’s perception of its worth for publicly traded firms, calculated by multiplying the share price by the total number of shares available. Following a company’s initial public offering (IPO) and subsequent listing on an exchange, its share price is dictated by supply and demand dynamics. Consequently, as market prices fluctuate, the market cap provides a current estimate of the company’s value.
For example:
ABC’ Company has 20,000 outstanding shares available for trading.
Each share of ‘ABC’ Company is priced at ₹20.
Market Cap = Current Share Price x Total Number of Shares Outstanding
Market Capitalization = ₹20 per share x 20,000 shares
Market Capitalization = ₹4,00,000
Therefore, the market capitalization of ‘ABC’ Company is ₹4,00,000
Large-Cap Equity Mutual Funds
Large-cap funds invest primarily in stocks of well-established companies with large market capitalizations. Investing in large-cap equity mutual funds means putting money into portfolios focused on the top 100 companies. These companies are industry leaders with proven track records, offering stability and lower volatility compared to small-cap stocks. Investing in large-cap funds offers potential for capital appreciation, steady compounding, and regular dividends. Large-cap funds are best for long-term investment. For example, TCS, Reliance and Infosys.
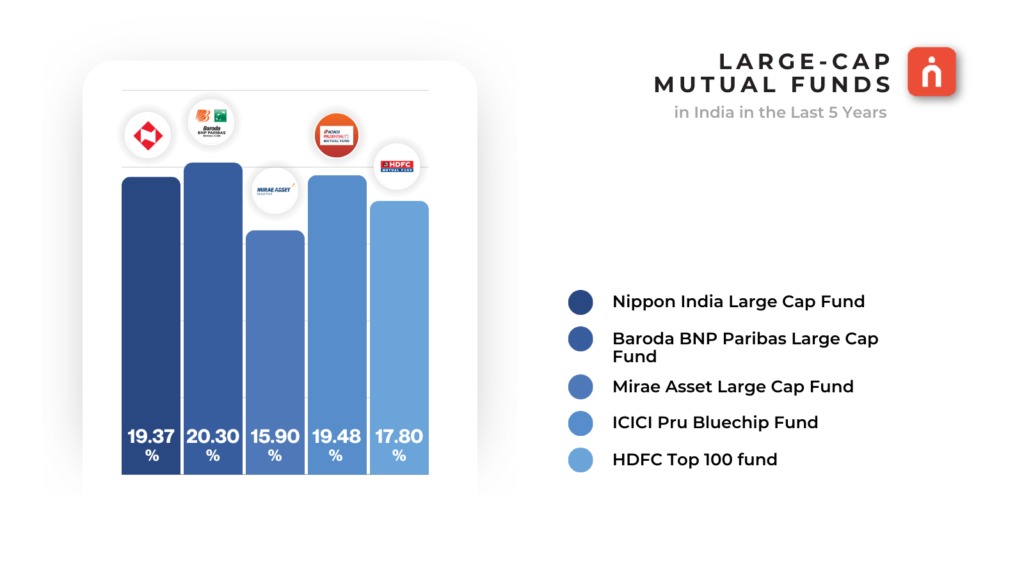
🔸Stability: Large-cap stocks are known for their stability and resilience, making them suitable for investors seeking capital preservation and consistent returns.
🔸Income Generation: Many large-cap companies pay dividends, providing investors with a source of income in addition to potential capital appreciation.
🔸Risk Mitigation: Large-cap funds can serve as core holdings in a diversified portfolio, helping to mitigate overall portfolio risk during market downturns.
🔸Suitable for Various Investors: Large-cap funds are suitable for investors with a moderate to low risk tolerance, including those nearing retirement or seeking a balanced approach to investing.
Small-Cap Equity Mutual Funds
Small-cap mutual funds primarily invest in small companies, typically ranking below 250th in market capitalization. These companies are new entrants in the market and tend to be highly volatile, carrying a high level of risk. However, they also offer significant return potential as they grow. Investors considering small-cap funds should have a higher risk tolerance and a longer investment horizon. These funds are best suited for those willing to withstand volatility and seek higher growth potential over time. For example, Jindal Steel & Power, Canara Bank and Mankind Pharma.
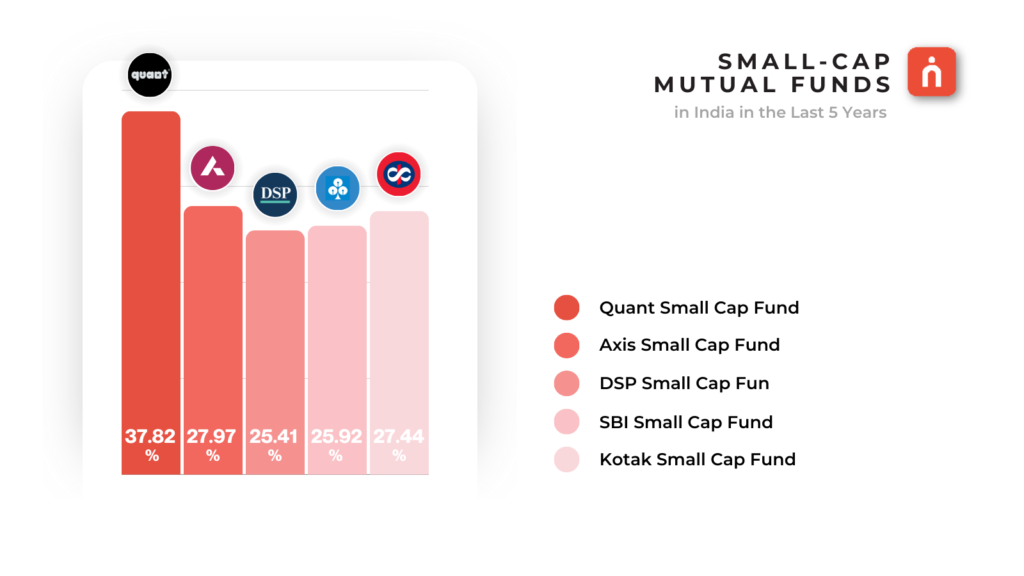
🔹Growth Potential: Small-cap stocks can offer significant growth potential, as these companies may be emerging with innovative products or services.
🔹Unpredictable: Due to their smaller size and early-stage nature, small-cap stocks tend to be more unpredictable and sensitive to market fluctuations.
🔹Long-Term investment duration: Investors with a high-risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon may consider small-cap funds as part of a diversified portfolio to capture potential long-term growth opportunities.
Small-Cap VS Large-Cap: A Comparative Overview for Investors
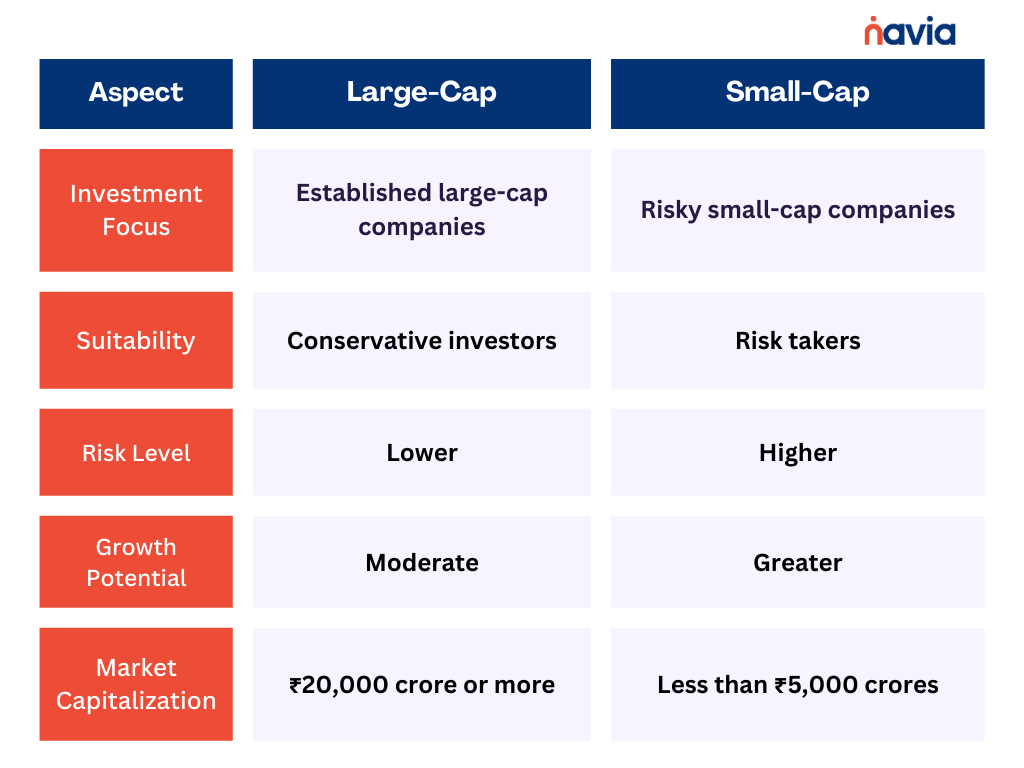
Choosing the Right Option
Both large-cap and small-cap funds possess distinct advantages and disadvantages that shape their characteristics and reactions to market changes. The best choice between these equity mutual funds depends on various factors, including an investor’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
Risk Tolerance Investors willing to tolerate higher volatility and seeking higher growth potential may lean towards small-cap funds, while those prioritizing stability and capital preservation may prefer large-cap funds.
Investment Duration Investors with a longer investment horizon can better weather the short-term volatility associated with small-cap funds and potentially benefit from their long-term growth prospects.
Portfolio Diversification A balanced approach to investing may involve allocating investments across both small-cap and large-cap funds, as well as other asset classes, to achieve diversification and manage risk effectively.

Conclusion
Choosing between small-cap and large-cap equity mutual funds requires careful consideration of individual financial circumstances and investment objectives. While small-cap funds offer higher growth potential but come with higher volatility, large-cap funds provide stability and income generation. Ultimately, investors should align their investment choices with their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and overall portfolio diversification strategy. Consulting with a financial advisor can help investors navigate the decision-making process and build a well-rounded investment portfolio tailored to their needs.
We’d Love to Hear from you