Understanding SEBI’s New Rules for Index Derivatives: What’s Changing for Traders?

We had on 28th August 2024 published a Blog titled “SEBI’s Consultation Paper on Index Derivatives Framework” which talked about the proposed measures SEBI is considering to restrict retail trading in Options
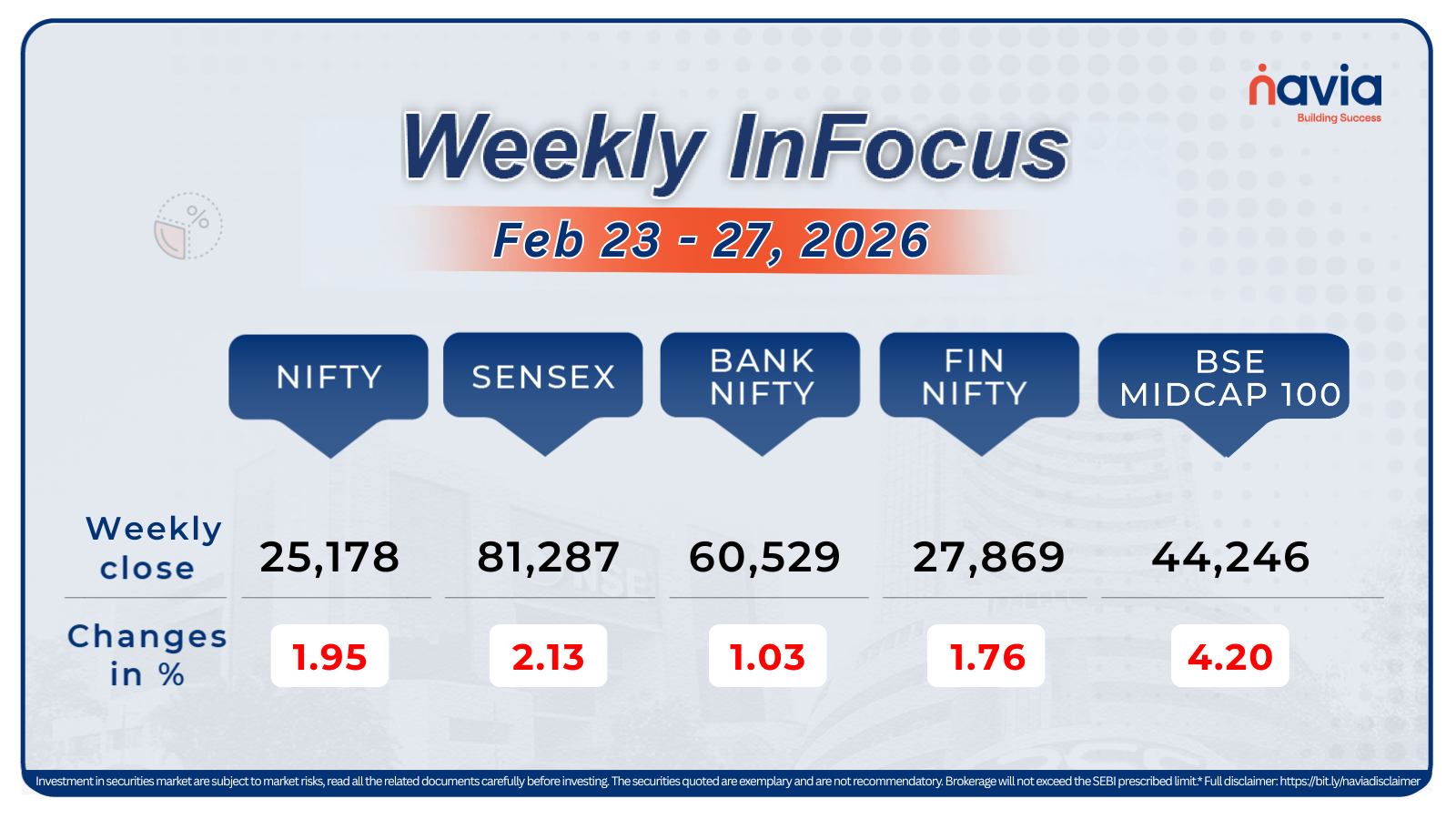
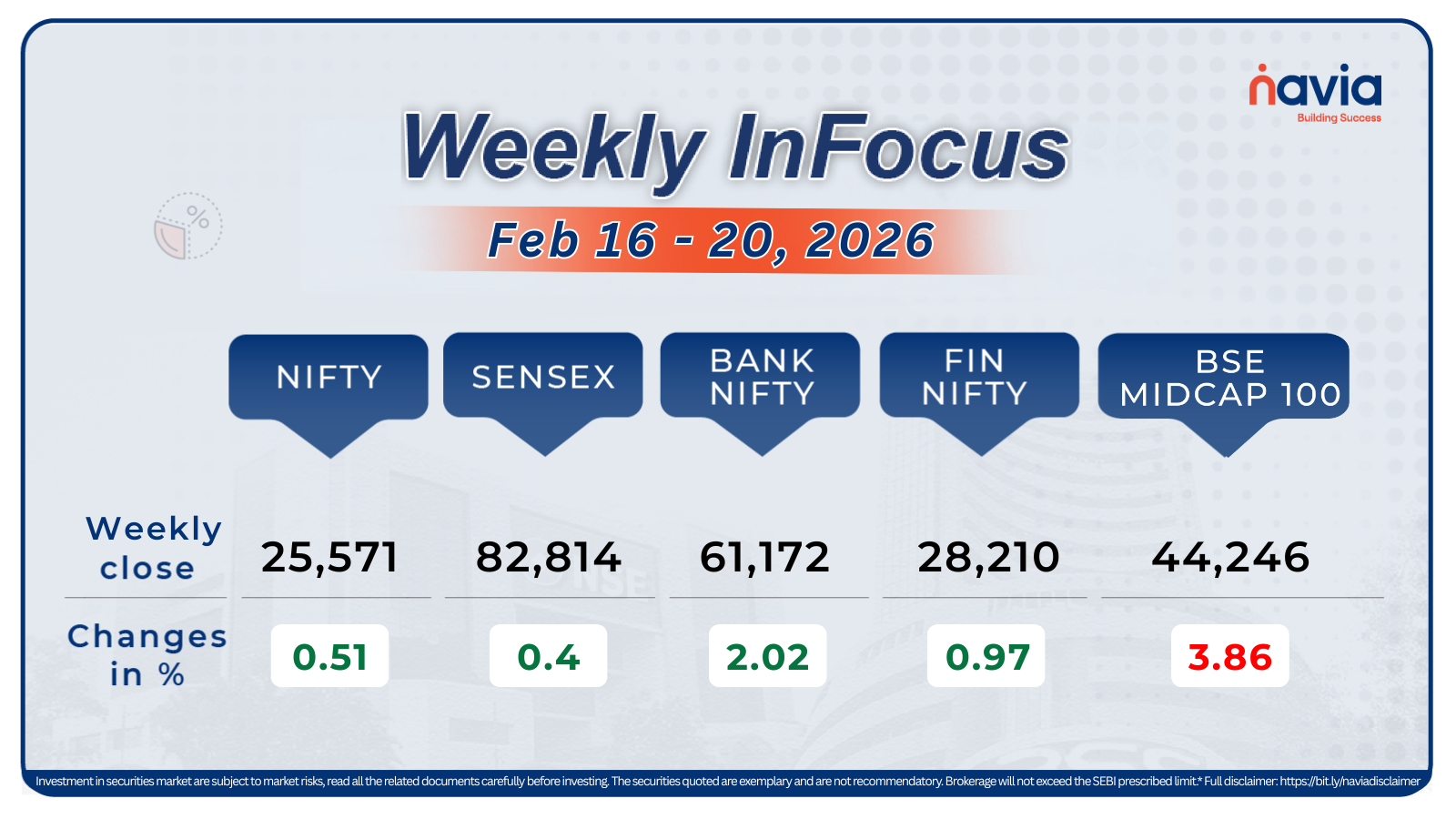
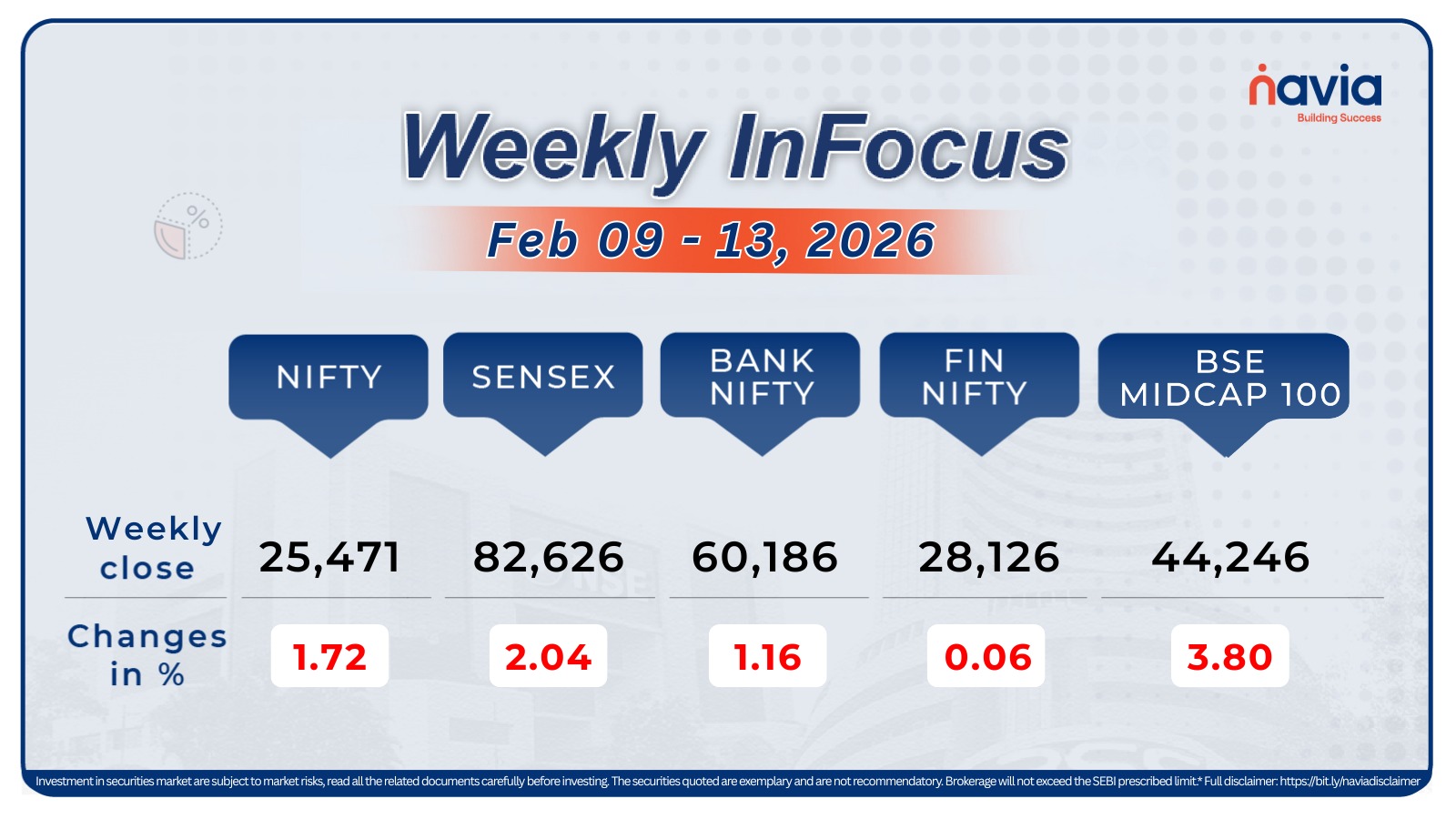
On October 1, 2024, SEBI released a circular that changes a few things for index derivatives. Here’s a breakdown of all the changes and their impact. Starting November 20, 2024, SEBI will introduce several important changes for derivative traders in an effort to increase investor protection and improve market stability. If you’re a trader dealing with index derivatives like Nifty, Sensex, BankNifty, FinNifty, Bankex, MidcpNifty, NiftyNXT50 these changes will directly impact how you trade options and futures. In this blog, we’ll explain these updates in simple terms, use examples, and provide a summary in tabular form for easy understanding.
Key Changes in SEBI’s Derivatives Regulations
Based on SEBI’s recent circular, the upcoming changes focus on margin requirements, contract sizes, expiry day trading, and more. Here’s what will change:
1. Increase in Contract Size
The contract value for Index F&O contracts will increase from the current range of Rs. 5 lakhs to Rs. 10 lakhs to a new range of Rs. 15 lakhs to Rs. 20 lakhs. To align with this change, the NSE and BSE will revise the lot sizes for all new index F&O contracts introduced on the effective date 21/11/24.
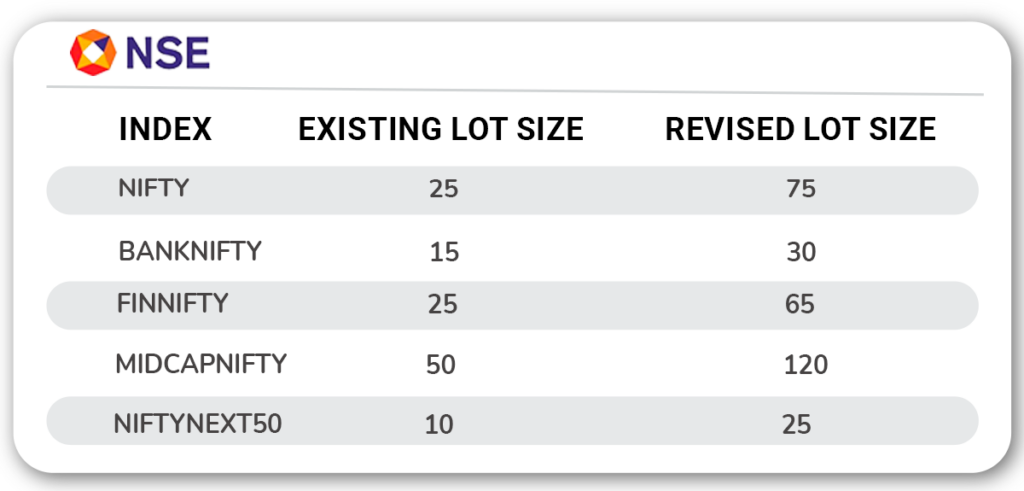
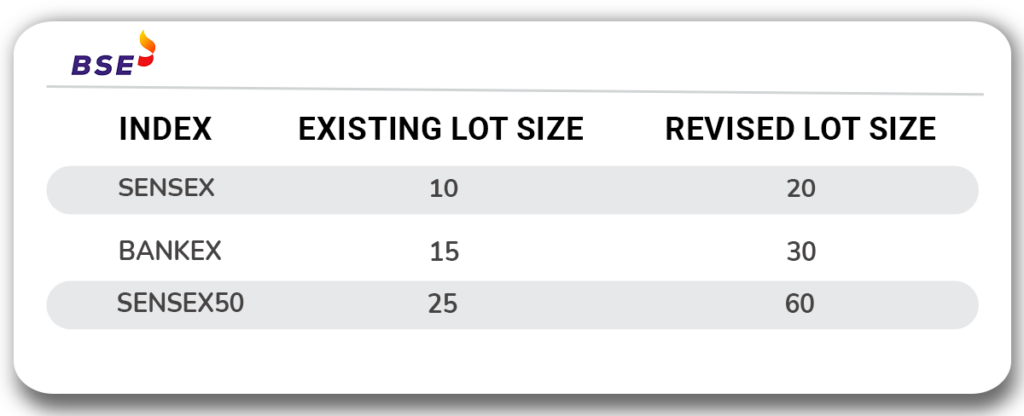
2. Revised Lot Sizes
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) will revise the lot sizes for all new index F&O contracts as in below from February 2025 contract expiry for Monthly contract and from January 2025 1st week for Weekly contracts.
NSE Indices:
BSE Indices:
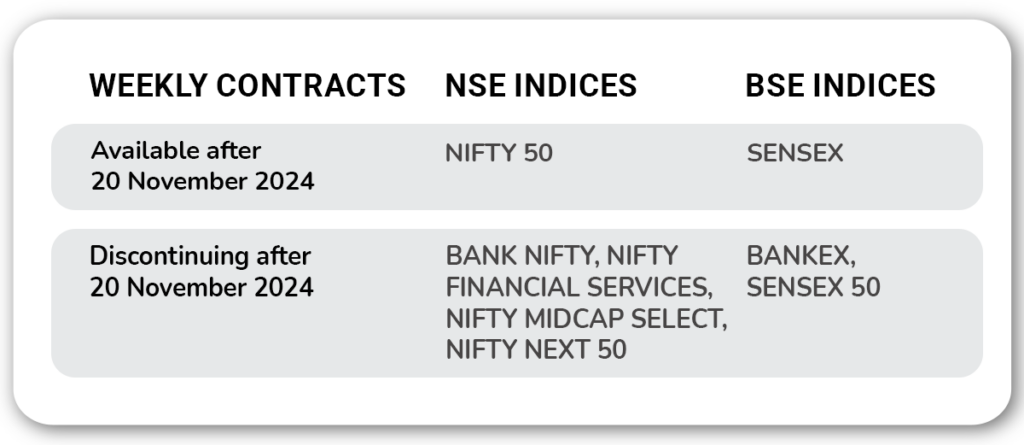
3. Limiting Weekly Expiry Contracts
As per the new rules, SEBI will restrict weekly expiry contracts to one benchmark index per exchange. This aims to reduce speculative trading and volatility on expiry days.
| Monthly Expiry Schedule for Index Options and Futures | ||||
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday |
| SENSEX50, BANKEX | Nifty50, FINNIFTY, BANKNIFTY,MIDCAPNIFTY, NIFTYNEXT50 | |||
| Individual Securities | ||||
| Weekly Expiry Schedule for Index Options | ||||
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday |
| Sensex | Nifty50 | |||
4. Increased Tail Risk Coverage on Expiry Day
To cover the risk of volatile price movements on expiry day, SEBI will require traders holding short positions to maintain an additional 2% Extreme Loss Margin (ELM) on expiry day. This new rule will be effective from November 20, 2024.
Example Calculation:
For a short position in a Nifty 25,000 call option:
● Strike Price: 25,000
● Lot Size: 25
2% Margin: Strike Price × Lot Size × 2% (25,000 * 25 * 2%) = 12,500
If the margin requirement for this position is Rs. 1 lakh, an additional margin of Rs. 12,500 will be required on the expiry day.
5. Upfront Collection of Options Premium
From February 1, 2025, traders will need to pay the full options premium upfront for buying options. Previously, traders could leverage smaller upfront margins to take larger positions, especially intraday. Now, traders must pay the entire premium at the time of the trade, reducing the excessive leverage some traders used.
6. Intraday Monitoring of Position Limits
From April 1, 2025, exchanges will begin to monitor position limits intraday rather than just at the end of the day. This means your positions will be checked at least four times daily to ensure they do not exceed permissible limits.
🔹 Example: If the limit for Nifty options is 1,000 contracts, the exchange will check your positions multiple times during the day. If your positions exceed this limit, you’ll need to bring them back within the limit or face penalties
Summary of Key Changes
| Measure | Effective Date | Impact on Traders |
|---|---|---|
| Revised Contract Size for Index Derivatives | November 20, 2024 | Contract value increased to at least ₹15 lakhs from February 2025 expiry onwards for monthly and from January 2025 1st week onwards for weekly contracts |
| Limiting Weekly Expiry Contracts | November 20, 2024 | Only 1 Index for weekly expiry from NSE and BSE. NIFTY weekly will expiry every Thursday and Sensex weekly will expire every Friday |
| Increased Tail Risk Coverage on Expiry Day | November 20, 2024 | Additional 2% margin required for short options on expiry day. |
| Upfront Collection of Options Premium | February 1, 2025 | Full premium required at the time of trade. |
| Removal of Calendar Spread on Expiry Day | February 1, 2025 | No margin benefit for spreads involving expiring contracts. |
| Intraday Monitoring of Position Limits | April 1, 2025 | Position limits will be monitored throughout the trading day. |
Impact on Traders and Examples
1. Reduced Leverage for Option Buyers
With the requirement to pay full premium upfront, traders will need more capital to take positions. This move limits excessive leverage and ensures better risk management.
2. Higher Margins on Expiry Days
On expiry days, traders will need to maintain higher margins as the calendar spread benefit is removed and additional tail risk coverage is introduced. This will require careful capital management to avoid margin calls.
3. Adjusted Contract Sizes
With Nifty trading at 25,000 and the contract size increasing to ₹15 lakhs, the number of contracts in each lot will increase to 60 (from lower levels), making it more capital-intensive for small traders to trade index derivatives.
4. Reduced Speculative Trading on Expiry
By offering only one weekly expiry index per exchange, SEBI aims to reduce speculation. With BSE choosing the Sensex (82,000) for weekly expiries, traders will need to adjust their strategies and focus on one index at a time.
How to Adapt to These Changes
To stay ahead of these new rules, traders should:
🔸 Plan ahead for expiry days, ensuring sufficient capital to cover increased margins.
🔸 Monitor position limits throughout the trading day to avoid penalties.
🔸 Adjust to the new contract sizes by trading more strategically or reducing position sizes.
🔸 Focus on Nifty weekly options on NSE and Sensex weekly options on BSE for expiration trades.
Conclusion
SEBI’s new regulations aim to make the index derivatives market safer and more stable by addressing excessive leverage, tightening margins, and reducing speculative volatility on expiry days. Traders will need to be more strategic in managing their positions, ensuring they have enough capital to meet the new margin requirements, and carefully selecting the right contracts.

With the changes coming into effect from November 20, 2024, now is the time to start adjusting your strategies and preparing for the new trading landscape.
By staying informed and adapting to these new rules, traders can continue to participate effectively in the derivatives market while navigating the tighter regulations.
We’d Love to Hear from you